Vertical Synchronization, commonly known as VSync, is a graphics technology that synchronizes the frame rate of a game with the refresh rate of a monitor to reduce screen tearing and improve visual quality. Understanding VSync, its benefits, and potential drawbacks is essential for optimizing your gaming experience, especially in fast-paced games like Fortnite. Also checkout this article Best FilterKeys Settings for Fortnite and don’t forget to download the FilterKeys Setter.
What is VSync?
VSync is a technology developed to address a common problem in gaming: screen tearing. Screen tearing occurs when the frame rate output by the graphics card is not synchronized with the refresh rate of the monitor, causing parts of multiple frames to be displayed simultaneously. This results in a visual artifact where the image on the screen appears disjointed, with horizontal lines separating different parts of the frame.

How VSync Works
VSync works by limiting the graphics card’s frame rate output to match the monitor’s refresh rate. For example, if you have a 60Hz monitor, It will cap the frame rate at 60 frames per second (fps). This synchronization prevents the graphics card from sending new frames before the monitor has finished displaying the current one, thus eliminating screen tearing.
Benefits of VSync
Improved Visual Quality
The primary benefit of VSync is the elimination of screen tearing, which results in a smoother and more visually appealing gaming experience. By synchronizing the frame rate with the monitor’s refresh rate, It ensures that each frame is displayed in its entirety before moving on to the next one.
Reduced Graphical Artifacts
In addition to screen tearing, It can also help reduce other graphical artifacts such as stuttering and ghosting. These issues are often caused by inconsistent frame rates and can be mitigated by the frame rate capping provided by VSync.
Enhanced Immersion
For games that prioritize visual fidelity over fast-paced action, VSync can enhance immersion by providing a consistent and stable visual experience. This is particularly beneficial in single-player games with high-quality graphics.
Drawbacks of VSync
While this may appear as a tear in the time-space continuum, that’s simply your GPU churning out frames faster than the maximum refresh rate of your monitor. Depending on how much your GPU’s frame rate exceeds your monitor’s refresh rate, you can see two or more GPU frames spliced horizontally during a single monitor refresh.
VSync eliminates screen tearing by limiting the GPU frame rate to the monitor’s refresh rate. However, that alone isn’t enough to prevent screen tearing. The setting also forces the frames rendered by the GPU to be displayed in conjunction with the monitor’s refresh cycle.
Stopping parts of multiple frames from being visible simultaneously is key to eliminating screen tearing. And VSync achieves that by preventing the GPU from pushing out new frames in the middle of the monitor’s refresh cycle.
Input Lag
One of the most significant drawbacks of VSync is the introduction of input lag. By capping the frame rate to match the monitor’s refresh rate, It can cause a delay between the player’s input and the corresponding action on the screen. This delay can be detrimental in fast-paced games where quick reactions are crucial, such as first-person shooters and competitive multiplayer games. But you can use Filter Keys to reduce Input Lags
Performance Overhead
Enabling VSync can also introduce a performance overhead, especially on lower-end systems. The process of synchronizing the frame rate with the refresh rate requires additional processing power, which can lead to a decrease in overall frame rates and potentially cause stuttering if the graphics card struggles to maintain the capped frame rate.
Compatibility Issues
VSync may not work well with all games or hardware configurations. Some games may experience stability issues or graphical glitches when It is enabled. Additionally, older monitors with lower refresh rates may not benefit as much from VSync, as the frame rate cap could be too restrictive.
Alternatives to VSync
To address the drawbacks of VSync, several alternative technologies have been developed, each offering different methods of synchronizing frame rates and improving visual quality without the associated issues.

G-Sync and FreeSync
G-Sync (by Nvidia) and FreeSync (by AMD) are adaptive sync technologies that dynamically adjust the monitor’s refresh rate to match the frame rate output by the graphics card. Unlike VSync, which caps the frame rate to match the refresh rate, adaptive sync technologies adjust the refresh rate to align with the current frame rate, providing a smoother and more responsive gaming experience without the significant input lag.
Benefits of Adaptive Sync
- Reduced Input Lag: By dynamically adjusting the refresh rate, adaptive sync technologies reduce the input lag associated with VSync.
- Eliminated Screen Tearing: Adaptive sync effectively eliminates screen tearing by ensuring that the monitor’s refresh rate matches the frame rate output by the graphics card.
- Improved Performance: Adaptive sync can improve overall performance by reducing the performance overhead associated with frame rate capping.
Fast Sync and Enhanced Sync
Fast Sync (by Nvidia) and Enhanced Sync (by AMD) are technologies designed to reduce screen tearing without introducing significant input lag. These technologies work by allowing the graphics card to render frames at a higher rate than the monitor’s refresh rate, but only displaying the most recent frame, thus reducing the visual artifacts and input lag associated with traditional VSync.
Benefits of Fast Sync and Enhanced Sync
- Lower Input Lag: By displaying only the most recent frame, these technologies significantly reduce input lag compared to traditional VSync.
- Minimal Screen Tearing: Although not entirely eliminating screen tearing, Fast Sync and Enhanced Sync greatly reduce its occurrence compared to having VSync disabled.
- Better Performance: These technologies provide a balance between visual quality and performance, making them suitable for competitive gaming.
How to Enable and Configure VSync
Enabling VSync in Game Settings
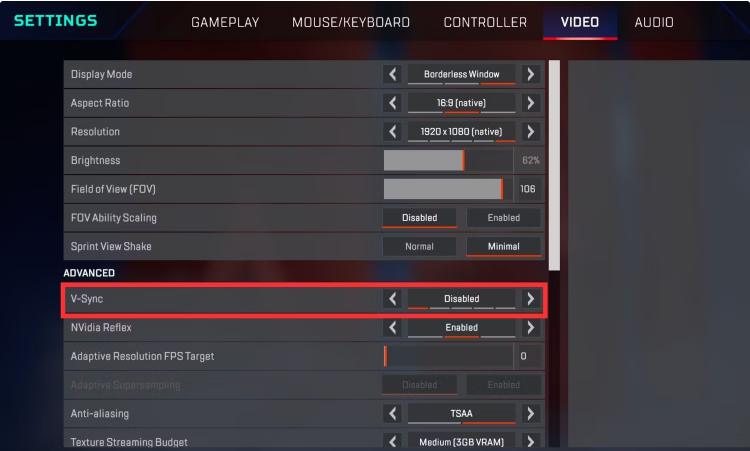
Most games provide an option to enable or disable VSync in their graphics settings menu. To enable VSync:
- Open Game Settings: Navigate to the graphics or display settings menu within the game.
- Enable VSync: Locate the VSync option and toggle it on.
- Adjust Additional Settings: Some games may offer additional options, such as triple buffering or adaptive VSync. Configure these settings based on your preferences and hardware capabilities.
Configuring VSync in GPU Control Panel
If you have a graphics card that supports VSync, you can easily enable it to ensure smooth performance on most displays. VSync can be activated either through the AMD FreeSync (AMF) technology or Nvidia graphics drivers. Alternatively, you can toggle the VSync setting within the graphics options of your game.
VSync can also be enabled and configured through the graphics card’s control panel. This provides more granular control over VSync settings and can be useful for overriding in-game settings.
Nvidia Control Panel
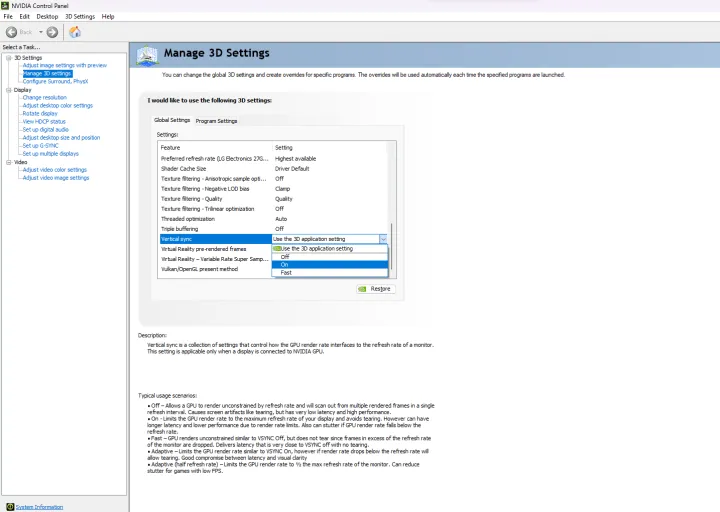
- Open Nvidia Control Panel: Right-click on your desktop and select “Nvidia Control Panel.”
- Manage 3D Settings: Navigate to the “Manage 3D Settings” section.
- Global Settings or Program Settings: Choose whether to apply VSync settings globally or to specific games.
- Vertical Sync: Locate the “Vertical Sync” option and select “On” to enable VSync.
AMD Radeon Software
- Open Radeon Software: Right-click on your desktop and select “AMD Radeon Software.”
- Graphics Settings: Navigate to the “Graphics” settings section.
- Wait for Vertical Refresh: Locate the “Wait for Vertical Refresh” option and select “Always On” to enable VSync.
When to Use VSync
Single-Player and Story-Driven Games
In single-player and story-driven games where visual quality and immersion are prioritized over competitive performance, VSync can enhance the gaming experience by eliminating screen tearing and providing a stable frame rate. Examples include action-adventure games, role-playing games, and simulation games.
High-Quality Graphics Settings
For games that push the limits of graphical fidelity, enabling VSync can help maintain visual integrity by synchronizing the frame rate with the monitor’s refresh rate. This is particularly beneficial for games with detailed textures, realistic lighting, and complex environments.
Older or Less Demanding Games
In older or less demanding games that can easily achieve frame rates higher than the monitor’s refresh rate, VSync can prevent excessive frame rates from causing screen tearing and other visual artifacts. This ensures a smooth and consistent gaming experience.
When to Avoid VSync
Competitive Multiplayer Games
In competitive multiplayer games where quick reactions and low input lag are crucial, it is generally advisable to avoid using VSync. The input lag introduced by VSync can hinder performance and put players at a disadvantage. Instead, consider using adaptive sync technologies or disabling VSync altogether.
High-Performance Gaming Systems
For high-performance gaming systems capable of maintaining high frame rates without screen tearing, the performance overhead and input lag introduced by VSync may outweigh its benefits. In such cases, disabling it or using alternative technologies like Fast Sync or Enhanced Sync can provide a better balance between performance and visual quality.
Optimizing Your Setup for Minimal Input Delay
Monitor and GPU Compatibility
Ensure your monitor and GPU are compatible with adaptive sync technologies like G-Sync or FreeSync. These technologies provide the best balance between reducing screen tearing and minimizing input lag, enhancing overall gaming performance.
Keep Drivers Updated
Regularly update your GPU drivers to ensure compatibility with the latest games and features. Updated drivers can also provide performance improvements and bug fixes that help reduce input delay and improve visual quality.
Customize In-Game Settings
Tailor in-game settings to your specific preferences and hardware capabilities. Experiment with different settings for VSync, adaptive sync, and frame rate limits to find the optimal configuration for your gaming experience.
Monitor Performance
Use performance monitoring tools to track frame rates, input lag, and overall system performance. This data can help you make informed decisions about which settings and technologies to use for the best gaming experience.
Conclusion
VSync is a valuable tool for enhancing visual quality and eliminating screen tearing in gaming. However, it comes with potential drawbacks such as input lag and performance overhead. Understanding the benefits and limitations, as well as exploring alternative technologies like G-Sync, FreeSync, Fast Sync, and Enhanced Sync, can help you optimize your gaming experience. By tailoring your settings and keeping your hardware and drivers updated, you can achieve a smoother, more responsive, and visually appealing gaming experience.